What, When, Where, How, Who?
Infinity
Introduction, Important Definitions and Related Concepts:
Infinity (commonly represented as the symbol ∞) comes from the
Latin
infinitas or "unboundedness.". Latin (lingua latīna,
pronounced
[laˈtiːna]) is an ancient
Indo-European language that was spoken in the
Roman Republic and the
Roman
Empire. Pronounced means Spoken; voiced. The Indo-European languages
comprise a
family of several hundred related
languages
and dialects,[1]
including most of the major languages of
Europe, the
northern
Indian subcontinent (South
Asia), the
Iranian plateau (Southwest
Asia), and much of
Central
Asia. The Roman Empire is the phase of the
ancient
Roman civilization characterized by an
autocratic
form of government. A republic is a
state or
country that
is not led by a hereditary
monarch,[1][2]
where the people of that state or country (or at least a part of that people)[3]
have impact on its government,[4]
and that is usually indicated as a republic.[5]
A family
is a domestic or social group. A language is a system of visual,
auditory, or tactile
symbols of
communication and the rules used to manipulate them. A dialect (from
the
Greek word διάλεκτος, dialektos) is a
variety of a
language
characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers.[1]
Europe is one of the seven traditional
continents
of the Earth.
Indian or Indians usually refers to the inhabitants of
India or,
alternatively and completely differently,
American Indians. A subcontinent is a small part of a
continent.
South means the direction along a meridian 90° clockwise from east; the
direction to the right of sunrise. Asia is the world's largest and most
populous
continent. Iran, (Persian:
ايران,[ʔiˈɾɒn]
ĭrănˈ), officially the
Islamic Republic of Iran (Persian:
جمهوری اسلامی ايران,
pronounced
[dʒomhuɾije ʔeslɒmije ʔiɾɒn]), formerly known internationally as
Persia until 1935, is a country in
Central Eurasia. In
geology and
earth
science, a plateau, also called a high plateau or tableland,
is an area of
highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. Southwest Abbr.
SW The direction or point on the mariner's compass halfway between
due south and due west, or 135° west of due north. Central means situated at,
in, or near the center: the central states. Ancient means
having had an existence of
many years. Civilization or civilisation is a kind
of human society
or culture;
specifically, a civilization is usually understood to be a
complex society characterized by the process of
state formation,
the practice of
agriculture and settlement in
cities. An
autocracy is a
form of government in which the
political power is held by a single self appointed ruler. A state is
a political
association with effective
sovereignty over a geographic
area. In
political geography and
international politics, a country is a
political division of a geographical entity, a
sovereign
territory, most commonly associated with the notions of
state or
nation and
government.
The word monarch derives from
Greek monos archein, meaning "one ruler," which referred to an
absolute ruler in
ancient Greece. Symbols are objects, characters, or other concrete
representations of ideas, concepts, or other abstractions. Communication
is a process that allows organisms to exchange information by several methods.
Greek (ελληνική γλώσσα
IPA:
[eliniˈkʲi ˈɣlosa] or
simply ελληνικά
IPA:
[eliniˈka] — "Hellenic")
has a documented history of 3,400 years, the longest of any single
natural language in the
Indo-European
language family. Variety means the quality or condition of being various or
varied; diversity. A continent is one of several large
landmasses
on Earth.
Earth (pronounced
/ˈɝːθ/[5])
is the third planet
from the Sun and is
the largest of the
terrestrial planets in the
Solar
System, in both
diameter
and mass. India
(Hindi: भारत
Bhārat; see also
other names), officially the Republic of India (Hindi:
भारत गणराज्य Bhārat Gaṇarājya),
is a sovereign nation in
South
Asia. The United
States of America is a
federal
constitutional republic comprising
fifty
states and a
federal district. Persian (local names: فارسی
[fɒɾˈsi], Fārsi or پارسی
[pɒɾˈsi], Pārsi; see
Nomenclature) is an
Indo-European
language
spoken in Iran (Persia),
Afghanistan,
Tajikistan,
Uzbekistan
and the
Persian Gulf states. Help means to give assistance to; aid: I helped her
find the book. He helped me into my coat. Generally speaking, the concept of
information is closely related to notions of
constraint,
communication,
control, data,
form,
instruction,
knowledge,
meaning,
mental
stimulus,
pattern,
perception,
and
representation. Islam (Arabic:
الإسلام; al-'islām )
is a
monotheistic
Abrahamic religion originating with the teachings of
Muhammad, a
7th century Arab
religious and political figure. The Persian Empire (Persian: امپراتوری
ایران) was a series of historical
empires that
ruled over the
Iranian plateau, the original Persian homeland, and beyond in
Western Asia,
Central
Asia, western
South Asia
and the
Caucasus. Eurasia is a large
landmass
covering roughly 53,990,000
km² which is 10.6 percent of the surface of the
Earth. Geology
(from Greek: γη, ge, "earth"; and λόγος,
logos,
"speech" lit. to talk about the earth) is the
science and
study of the solid matter that constitutes the
Earth. Science
(from the Latin scientia, 'knowledge'),
in the broadest sense, refers to any
systematic
knowledge or
practice.
Highland (geography), an elevated mountainous region. A society is a
grouping of
individuals
which is characterized by common interests and may have distinctive
culture and
institutions. Culture (from the
Latin cultura
stemming from colere, meaning "to cultivate,") generally refers to
patterns of human activity and the symbolic structures that give such activities
significance and importance. Complex means consisting of interconnected or
interwoven parts; composite. Agriculture is the production of
food,
feed,
fiber and other
goods by the systematic growing/harvesting of
plants,
animals and
other life forms. A city is an
urban
settlement with a particularly important status which differentiates it from a
town. Form (Lat.
forma
Eng. mould), refers to the external
three-dimensional outline, appearance or configuration of some thing - in
contrast to the matter or content or substance of which it is composed (compare
with shape). A
government is "the organization, that is the governing authority of a
political unit,"[1]
"the ruling power in a political society,"[2]
Politics is the process by which groups of people make decisions.
Political power, power held by a person or group in a country's political
system.
Voluntary association, a group of individuals who voluntarily enter into an
agreement to accomplish a purpose. Sovereignty is the exclusive
right to complete
control over an area of governance, people, or oneself. Area is a
quantity
expressing the two-dimensional
size of a defined part of a
surface,
typically a region bounded by a closed
curve.
Geography is the study of the
earth and its
features, inhabitants, and phenomena.[1]
International or internationally most often describes
interaction between
nations, or encompassing two or more nations, constituting a group or
association having members in two or more nations, or generally reaching beyond
national boundaries. Specifically, if c times b equals a,
written:
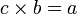 where b is not
zero,
then a divided by b equals c, written:
where b is not
zero,
then a divided by b equals c, written:
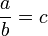 .
A territory (from the word 'terra', meaning 'land') is a defined area
(including land and waters),considered to be a possession of a person,
organization, institution, animal,
state or
country subdivision. A nation is a form of self-defined cultural and
social community. Greece (Greek:
Ελλάδα Elláda,
IPA:
[ɛˈlaða], or Ελλάς
Ellás,
[ɛˈlas]), officially the Hellenic Republic [Ελληνική Δημοκρατία
(ɛliniˈkʲi ðimokraˈtia)],[3]
is a country
in Southeastern Europe, situated on the southern end of the
Balkan Peninsula.
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)[I]
is a system of
phonetic notation based on the
Latin alphabet, devised by the
International Phonetic Association as a standardized representation of the
sounds of spoken language.[1]
Natural means present in or produced by nature:
a natural pearl. A landmass is a large continuous area of
land. A
planet, as
defined by the
International Astronomical Union (IAU), is a celestial body
orbiting a
star or
stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own
gravity, not massive enough to cause
thermonuclear fusion, and has
cleared its neighbouring region of
planetesimals.[1][2]
The Sun (Latin:
Sol) is the
star at the center
of the
Solar System.
Terrestrial planet, a planet that is primarily composed of silicate rocks.
Solar means f, relating to, or proceeding from the sun: solar rays; solar
physics. System (from
Latin systēma,
in turn from
Greek σύστημα systēma) is a
set of interacting or
interdependent
entities, real or abstract, forming an integrated whole. In
geometry, a
diameter (Greek
words dia = through and metro = measure) of a
circle is any
straight
line
segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose
endpoints
are on the circle. Mass is a fundamental concept in
physics,
roughly corresponding to the intuitive idea of "how much matter there is in an
object". Hindi (Devanāgarī:
हिन्दी or
हिंदी,
IAST:
Hindī,
IPA:
[hɪnd̪iː] )
is the name given to an
Indo-Aryan language, or a
dialect continuum of languages, spoken in
northern
and
central India
(the "Hindi
belt"),[4]
The Other or constitutive other (also referred to as
othering) is a key concept in
continental philosophy, opposed to the
Same. Federal means of, relating to, or being a form of government in
which a union of states recognizes the sovereignty of a central authority while
retaining certain residual powers of government. A constitution is a
system for governance, often
codified as a written document, that establishes the rules and principles of
an autonomous political entity. 50 (fifty) is the
integer
following
49
and preceding
51.
Local government areas called districts are used, or have been used,
in several countries. Nomenclature refers to a set or system of names or
terms, as those used in a particular science or art, used by an individual or
community.[1]
Afghanistan, officially the
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (Pashto:
د افغانستان اسلامي جمهوریت,
Persian: جمهوری اسلامی افغانستان), is a
landlocked country that is located approximately in the center of
Asia. Tajikistan
(pronounced
/təˈdʒɪkɨstæn/ or
/təˈdʒiːkɨstæn/;
Tajik: Тоҷикистон,
pronounced
[tɔʤikɪsˈtɔn] or
[tɒːʤikɪsˈtɒn]), officially, the Republic of Tajikistan (Tajik:
Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон) is a
mountainous
landlocked country in
Central
Asia. Uzbekistan, officially the Republic of Uzbekistan (Uzbek:
O‘zbekiston Respublikasi or Ўзбекистон Республикаси;
Russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly
landlocked country in
Central
Asia, formerly part of the
Soviet
Union. A
bay, usually referring to a large bay that is an arm of an
ocean or
sea. Constraint means
the state of being
checked, restricted, or compelled to avoid or perform some action
<the constraint and monotony of a monastic life —
Matthew Arnold>. Control is used in a variety of
contexts to express "mastery" or "proficiency":
e.g. "Music students attending a master class are expected to have full control
of basic skills such as rhythm and pitch". Data refers to a collection of
organized
information, usually the results of
experience,
observation or
experiment,
or a set of
premises. An instruction is a form of
communicated
information that is both
command
and
explanation for how an
action,
behavior, method, or
task is to be
begun, completed, conducted, or executed. Knowledge is defined (Oxford
English Dictionary) variously as (i) expertise, and skills acquired by a
person through
experience
or education;
the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject, (ii) what is known in a
particular field or in total; facts and information or (iii) awareness or
familiarity gained by experience of a fact or situation.
Meaning (linguistic), meaning which is communicated through the use of
language. Mind, the
collective aspects of intellect and consciousness.
Stimulus (physiology), something external that influences an activity. A
pattern, from the
French patron, is a theme of reoccurring events or objects, sometimes
referred to as elements of a set. In
psychology
and the
cognitive sciences, perception is the process of acquiring,
interpreting, selecting, and organizing
sensory
information.
Knowledge representation, the study of formal ways to describe knowledge.
Arabic (الْعَرَبيّة
al-ʿarabiyyah or just عَرَبيْ
ʿarabī) is the largest living member of the
Semitic language family in terms of speakers. In
theology,
monotheism (from
Greek
μόνος "one" and
θεός "god")
is the belief in the existence of one
deity, or in the
oneness of God.[1]
Abrahamic religion is a term commonly used to designate the three
prevalent
monotheistic religions—Christianity,
Islam, and
Judaism[1][2]—which
claim Abraham
(Hebrew:
Avraham אַבְרָהָם ;
Arabic: Ibrahim ابراهيم ) as a part of their sacred history. Abu
l-Qasim Muhammad
ibn
‘Abd Allāh al-Hashimi al-Qurashi (Arabic:
محمد[2]
Muḥammad; (Mohammed, Muhammed, Mahomet)[3][4][5]
(c. 570 Mecca –
June 8,
632
Medina),[6]
was the founder of
Islam and is regarded by
Muslims as the
last messenger and
prophet of
God (Arabic: الله
Allah), and is also regarded as a prophet by the
Druze and as a
Manifestation of God by the
Bahá'í
Faith.[7]
An Arab (Arabic:
عربي, ʿarabi) is a member of
an
ethnic group which
identifies as such on the basis of either
genealogical
or
linguistic grounds, sometimes including
Arabized
populations. The Western is a fiction
genre seen in
film,
television,
radio,
literature,
painting
and other
visual arts. A caucus is most generally defined as a meeting of
supporters or members of a
political party or movement. Square kilometre (U.S.
spelling: square kilometer), symbol km2, is a decimal
multiple of the SI
unit of
surface
area, the
square
metre, one of the
SI derived units. Logos derives from the verb
λέγω legō: to count, tell, say, or speak.[1]
Systematic means
presented or formulated as a coherent body of ideas or principles
<systematic thought>.
Practice (learning method), a method of learning by repetition. Grouping
means a collection of people or things united into a group.
.
A territory (from the word 'terra', meaning 'land') is a defined area
(including land and waters),considered to be a possession of a person,
organization, institution, animal,
state or
country subdivision. A nation is a form of self-defined cultural and
social community. Greece (Greek:
Ελλάδα Elláda,
IPA:
[ɛˈlaða], or Ελλάς
Ellás,
[ɛˈlas]), officially the Hellenic Republic [Ελληνική Δημοκρατία
(ɛliniˈkʲi ðimokraˈtia)],[3]
is a country
in Southeastern Europe, situated on the southern end of the
Balkan Peninsula.
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)[I]
is a system of
phonetic notation based on the
Latin alphabet, devised by the
International Phonetic Association as a standardized representation of the
sounds of spoken language.[1]
Natural means present in or produced by nature:
a natural pearl. A landmass is a large continuous area of
land. A
planet, as
defined by the
International Astronomical Union (IAU), is a celestial body
orbiting a
star or
stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own
gravity, not massive enough to cause
thermonuclear fusion, and has
cleared its neighbouring region of
planetesimals.[1][2]
The Sun (Latin:
Sol) is the
star at the center
of the
Solar System.
Terrestrial planet, a planet that is primarily composed of silicate rocks.
Solar means f, relating to, or proceeding from the sun: solar rays; solar
physics. System (from
Latin systēma,
in turn from
Greek σύστημα systēma) is a
set of interacting or
interdependent
entities, real or abstract, forming an integrated whole. In
geometry, a
diameter (Greek
words dia = through and metro = measure) of a
circle is any
straight
line
segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose
endpoints
are on the circle. Mass is a fundamental concept in
physics,
roughly corresponding to the intuitive idea of "how much matter there is in an
object". Hindi (Devanāgarī:
हिन्दी or
हिंदी,
IAST:
Hindī,
IPA:
[hɪnd̪iː] )
is the name given to an
Indo-Aryan language, or a
dialect continuum of languages, spoken in
northern
and
central India
(the "Hindi
belt"),[4]
The Other or constitutive other (also referred to as
othering) is a key concept in
continental philosophy, opposed to the
Same. Federal means of, relating to, or being a form of government in
which a union of states recognizes the sovereignty of a central authority while
retaining certain residual powers of government. A constitution is a
system for governance, often
codified as a written document, that establishes the rules and principles of
an autonomous political entity. 50 (fifty) is the
integer
following
49
and preceding
51.
Local government areas called districts are used, or have been used,
in several countries. Nomenclature refers to a set or system of names or
terms, as those used in a particular science or art, used by an individual or
community.[1]
Afghanistan, officially the
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (Pashto:
د افغانستان اسلامي جمهوریت,
Persian: جمهوری اسلامی افغانستان), is a
landlocked country that is located approximately in the center of
Asia. Tajikistan
(pronounced
/təˈdʒɪkɨstæn/ or
/təˈdʒiːkɨstæn/;
Tajik: Тоҷикистон,
pronounced
[tɔʤikɪsˈtɔn] or
[tɒːʤikɪsˈtɒn]), officially, the Republic of Tajikistan (Tajik:
Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон) is a
mountainous
landlocked country in
Central
Asia. Uzbekistan, officially the Republic of Uzbekistan (Uzbek:
O‘zbekiston Respublikasi or Ўзбекистон Республикаси;
Russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly
landlocked country in
Central
Asia, formerly part of the
Soviet
Union. A
bay, usually referring to a large bay that is an arm of an
ocean or
sea. Constraint means
the state of being
checked, restricted, or compelled to avoid or perform some action
<the constraint and monotony of a monastic life —
Matthew Arnold>. Control is used in a variety of
contexts to express "mastery" or "proficiency":
e.g. "Music students attending a master class are expected to have full control
of basic skills such as rhythm and pitch". Data refers to a collection of
organized
information, usually the results of
experience,
observation or
experiment,
or a set of
premises. An instruction is a form of
communicated
information that is both
command
and
explanation for how an
action,
behavior, method, or
task is to be
begun, completed, conducted, or executed. Knowledge is defined (Oxford
English Dictionary) variously as (i) expertise, and skills acquired by a
person through
experience
or education;
the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject, (ii) what is known in a
particular field or in total; facts and information or (iii) awareness or
familiarity gained by experience of a fact or situation.
Meaning (linguistic), meaning which is communicated through the use of
language. Mind, the
collective aspects of intellect and consciousness.
Stimulus (physiology), something external that influences an activity. A
pattern, from the
French patron, is a theme of reoccurring events or objects, sometimes
referred to as elements of a set. In
psychology
and the
cognitive sciences, perception is the process of acquiring,
interpreting, selecting, and organizing
sensory
information.
Knowledge representation, the study of formal ways to describe knowledge.
Arabic (الْعَرَبيّة
al-ʿarabiyyah or just عَرَبيْ
ʿarabī) is the largest living member of the
Semitic language family in terms of speakers. In
theology,
monotheism (from
Greek
μόνος "one" and
θεός "god")
is the belief in the existence of one
deity, or in the
oneness of God.[1]
Abrahamic religion is a term commonly used to designate the three
prevalent
monotheistic religions—Christianity,
Islam, and
Judaism[1][2]—which
claim Abraham
(Hebrew:
Avraham אַבְרָהָם ;
Arabic: Ibrahim ابراهيم ) as a part of their sacred history. Abu
l-Qasim Muhammad
ibn
‘Abd Allāh al-Hashimi al-Qurashi (Arabic:
محمد[2]
Muḥammad; (Mohammed, Muhammed, Mahomet)[3][4][5]
(c. 570 Mecca –
June 8,
632
Medina),[6]
was the founder of
Islam and is regarded by
Muslims as the
last messenger and
prophet of
God (Arabic: الله
Allah), and is also regarded as a prophet by the
Druze and as a
Manifestation of God by the
Bahá'í
Faith.[7]
An Arab (Arabic:
عربي, ʿarabi) is a member of
an
ethnic group which
identifies as such on the basis of either
genealogical
or
linguistic grounds, sometimes including
Arabized
populations. The Western is a fiction
genre seen in
film,
television,
radio,
literature,
painting
and other
visual arts. A caucus is most generally defined as a meeting of
supporters or members of a
political party or movement. Square kilometre (U.S.
spelling: square kilometer), symbol km2, is a decimal
multiple of the SI
unit of
surface
area, the
square
metre, one of the
SI derived units. Logos derives from the verb
λέγω legō: to count, tell, say, or speak.[1]
Systematic means
presented or formulated as a coherent body of ideas or principles
<systematic thought>.
Practice (learning method), a method of learning by repetition. Grouping
means a collection of people or things united into a group.
