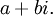What, When, Where, How. Who?
Many-Worlds Interpretation (MWI)
Introduction, Important Definitions and Related Concepts:
The many-worlds interpretation or MWI (also known as relative state formulation, theory of the universal wavefunction, many-universes interpretation or many worlds), is an interpretation of quantum mechanics. Many-worlds denies the objective reality of wavefunction collapse. Language interpreting or interpretation is the intellectual activity of facilitating oral and sign-language communication, either simultaneously or consecutively, between two, or among three or more, speakers who neither speak nor sign the same source language. Functionally, interpreting and interpretation are the descriptive words for the activity; in professional practice interpreting denotes spoken language, while interpretation denotes translation studies work. In physics, a quantum (plural: quanta) is an indivisible entity of energy. A photon, for instance, being a unit of light, is a "light quantum." Mechanics (Greek Μηχανική) is the branch of physics concerned with the behaviour of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effect of the bodies on their environment. The discipline has its roots in several ancient civilizations: ancient Greece, where Aristotle studied the way bodies behaved when they were thrown through the air (e.g. a stone); ancient China, with figures such as Zhang Heng, Shen Kuo, and Su Song; and ancient India, with thinkers such as Kanada, Aryabhata, and Brahmagupta. The term "objectivity" designates both a feature of scientific investigators and a feature of scientific inquiry itself. To be objective is to adhere strictly to truth- conducive methods in one's thinking, particularly, to take into account all available information, and to avoid any form of prejudice, bias, or wishful thinking. Reality, in everyday usage, means "the state of things as they actually exist." [1] [2] The term reality, in its widest sense, includes everything that is, whether or not it is observable or comprehensible. A wave function is a mathematical tool used in quantum mechanics to describe any physical system. It is a function from a space that consists of the possible states of the system into the complex numbers. Collapse means
A restating of something in other, especially simpler, words: paraphrase, rendering, restatement, version. See words. The process or result of changing from one appearance, state, or phase to another: change, changeover, conversion, metamorphosis, mutation, shift, transfiguration, transformation, transmogrification, transmutation, transubstantiation. See change/persist.
- Studying, The pursuit of knowledge, as by reading, observation, or research. Study (drawing), a drawing, sketch or painting done in preparation for a finished piece. Physics is the science of matter[1] and its motion,[2][3] as well as space and time[4][5] — the science that deals with concepts such as force, energy, mass, and charge. Physics is an experimental science;[6] it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the world around us behaves.[7] An entity is something that has a distinct, separate existence, though it need not be a material existence. In particular, abstractions and legal fictions are usually regarded as entities. In physics, the photon is the elementary particle (specifically, a boson) responsible for electromagnetic phenomena. It is the carrier of electromagnetic radiation of all wavelengths, including gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves. Light, or visible light, is electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength that is visible to the human eye (about 400–700 nm). In a scientific context, the word light is sometimes used to refer to the entire electromagnetic spectrum.[1] Greek (ελληνική γλώσσα IPA: [eliniˈkʲi ˈɣlosa] or simply ελληνικά IPA: [eliniˈka] — "Hellenic") has a documented history of 3,400 years, the longest of any single natural language in the Indo-European language family. It is also one of the earliest attested Indo-European languages, with fragmentary records in Mycenaean dating back to the 15th or 14th century BC, making it one of the world's oldest recorded living languages. Physical means The nature (physicality) of a physical entity
-
Physical examination, a regular overall
check-up with a doctor. With regard to
living things, a body is the
integral physical material of an individual.
"Body" often is used in connection with
appearance,
health issues and
death. In
physics, force is what causes a
mass to
accelerate. It may be experienced as a
twist, a push, or a pull.
-
Particle displacement, a measurement
of distance of the movement of a
particle in a medium as it transmits a
wave.
Displacement field (mechanics), an
assignment of displacement vectors for
all points in a body that is displaced
from one state to another. Ancient means
having had
an existence of many years2: of
or relating to a remote period, to a
time early in history, or to those
living in such a period or time;
especially
: of
or relating to the historical period
beginning with the earliest known
civilizations and extending to the fall
of the western Roman Empire in
a.d. 476.
Greece (Greek:
Ελλάδα,
Elláda,
IPA:
[ɛˈlaða], or Ελλάς, Ellás,
[ɛˈlas]), officially the
Hellenic Republic [Ελληνική
Δημοκρατία
(ɛliniˈkʲi ðimokraˈtia)],[3]
is a
country in Southeastern Europe,
situated on the southern end of the
Balkan Peninsula. It has borders
with
Albania, the (former Yugoslav)
Republic of Macedonia and
Bulgaria to the north, and
Turkey to the east. Aristotle
(Greek:
Ἀριστοτέλης Aristotélēs)
(384 BC – 322 BC) was a
Greek
philosopher, a student of
Plato and teacher of
Alexander the Great. He wrote on
many different subjects, including
physics,
metaphysics,
poetry,
theater,
music,
logic,
rhetoric,
politics,
government,
ethics,
biology and
zoology. China (traditional
Chinese:
中國;
simplified Chinese:
中国;
Hanyu Pinyin:
Zhōngguó ;
Tongyong Pinyin:
Jhongguó;
Wade-Giles (Mandarin):
Chung¹kuo²) is a
cultural region, an ancient
civilization, and a
national or
multinational entity in
East Asia. The civilization is one
of the world's oldest, consisting of
states and
cultures dating back more than six
millennia. Zhang Heng (Chinese:
張衡;
pinyin:
Zhāng
Héng;
Wade-Giles: Chang Heng) (AD
78–139)
was an
astronomer,
mathematician,
inventor,
geographer,
artist,
poet,
statesman, and
literary scholar of the
Eastern Han Dynasty in ancient
China. He had extensive knowledge of
mechanics and gears, applying this
knowledge to several of his known
inventions. Shen Kuo or Shen
Kua (Chinese:
沈括;
pinyin:
Shěn Kuò)
(1031–1095) was a
polymathic
Chinese
scientist and statesman of the
Song Dynasty (960–1279). Excelling
in many fields of study and statecraft,
he was a
mathematician,
astronomer,
meteorologist,
geologist,
zoologist,
botanist,
pharmacologist,
agronomist,
archaeologist,
ethnographer,
cartographer,
encyclopedist,
general,
diplomat,
hydraulic engineer,
inventor,
academy chancellor,
finance minister, governmental state
inspector, poet, and musician..
Su Song (traditional Chinese: 蘇頌; simplified Chinese: 苏颂; pinyin: Sū Sòng; style Zirong 子容) (1020–1101 AD) was a renowned Chinese statesman, astronomer, cartographer, horologist, pharmacologist, mineralogist, zoologist, botanist, mechanical and architectural engineer, and ambassador of the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD).
Su Song was the engineer of a water-driven astronomical clock tower in medieval Kaifeng, which employed the use of an early escapement mechanism.[2][3][4][5] India (Hindi: भारत Bhārat; see also other names), officially the Republic of India (Hindi: भारत गणराज्य Bhārat Gaṇarājya), is a sovereign nation in South Asia. It is the seventh largest country by geographical area, the second most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world.[12] Kanada (also transliterated as Canada and in other ways; Sanskrit कणाद) was a Hindu sage who founded the philosophical school of Vaisheshika. [1]. He talked of Dvyanuka (biatomic molecule) and tryanuka (triatomic molecule). Āryabhaṭa (Devanāgarī: आर्यभट) (b. 476 AD – 550) is the first in the line of great mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His most famous works are the Aryabhatiya (499) and Arya-Siddhanta. Brahmagupta was born in 598 CE in Bhinmal city in the state of Rajasthan of northwest India. He likely lived most of his life in Bhillamala (modern Bhinmal in Rajasthan) in the empire of Harsha during the reign (and possibly under the patronage) of King Vyaghramukha.[1] In physics, particularly in quantum physics, a system observable is a property of the system state that can be determined by some sequence of physical operations. For example, these operations might involve submitting the system to various electromagnetic fields and eventually reading a value off some gauge. Comprehensible means readily comprehended or understood; intelligible. The mathematical concept of a function expresses dependence between two quantities, one of which is given (the independent variable, argument of the function, or its "input") and the other produced (the dependent variable, value of the function, or "output"). A function associates a single output to each input element drawn from a fixed set, such as the real numbers. Science considers space to be a fundamental quantity (a quantity which can not be defined via other quantities because other quantities — like force and energy — are already defined via space). Thus an operational definition is used in which the procedure of measurement of space intervals (distances) and the units of measurement are defined.
In mathematics, a complex number is a number which can be formally defined as an ordered pair of real numbers (a,b), often written:
Complex numbers have addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations defined, with behaviours which are a strict superset of real numbers, as well as having other elegant and useful properties. Symbols are objects, characters, or other concrete representations of ideas, concepts, or other abstractions. For example, in the United States, Canada, Australia and Great Britain, a red octagon is a symbol for the traffic sign meaning "STOP". Communication is a process that allows organisms to exchange information by several methods. Exchange requires feedback. Phenomenon meansan object or aspect known through the senses rather than by thought or intuition. A temporal or spatiotemporal object of sensory experience as distinguished from a noumenon. Paraphrase (IPA: /ˈpærəˌfreɪz/) is restatement of a text or passage, using other words. The term "paraphrase" derives via the Latin "paraphrasis" from the Greek "para phraseïn" ("additional manner of expression"). Rendering is the process of generating an image from a model, by means of computer programs. The model is a description of three dimensional objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. Restate means to state again or in a new form. See Synonyms at repeat.
A version is any change in form.
For the process of assigning software version numbers, see Software versioning. Word meansA sound or a combination of sounds, or its representation in writing or printing, that symbolizes and communicates a meaning and may consist of a single morpheme or of a combination of morphemes. Something said; an utterance, remark, or comment: May I say a word about that? Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz harnessed mathematical concepts into calculus to provide mathematical models of change. In modern physics, the concept of change is associated with action. Changeover in manufacturing is the process of converting a line or machine from running one product to another. Changeover times can last from a few minutes to as much as several weeks in the case of automobile manufacturers retooling for new models. Conversion meansSomething that is changed from one use, function, or purpose to another.
- Law. The unlawful
appropriation of another's
property. Metamorphosis means
any complete change in appearance, character, circumstances, etc. a form resulting from any such change.
Next
-
-
Particle displacement, a measurement
of distance of the movement of a
particle in a medium as it transmits a
wave.
Displacement field (mechanics), an
assignment of displacement vectors for
all points in a body that is displaced
from one state to another. Ancient means
having had
an existence of many years2: of
or relating to a remote period, to a
time early in history, or to those
living in such a period or time;
especially
: of
or relating to the historical period
beginning with the earliest known
civilizations and extending to the fall
of the western Roman Empire in
a.d. 476.
Greece (Greek:
Ελλάδα,
Elláda,
IPA:
[ɛˈlaða], or Ελλάς, Ellás,
[ɛˈlas]), officially the
Hellenic Republic [Ελληνική
Δημοκρατία
(ɛliniˈkʲi ðimokraˈtia)],[3]
is a
country in Southeastern Europe,
situated on the southern end of the
Balkan Peninsula. It has borders
with
Albania, the (former Yugoslav)
Republic of Macedonia and
Bulgaria to the north, and
Turkey to the east. Aristotle
(Greek:
Ἀριστοτέλης Aristotélēs)
(384 BC – 322 BC) was a
Greek
philosopher, a student of
Plato and teacher of
Alexander the Great. He wrote on
many different subjects, including
physics,
metaphysics,
poetry,
theater,
music,
logic,
rhetoric,
politics,
government,
ethics,
biology and
zoology. China (traditional
Chinese:
中國;
simplified Chinese:
中国;
Hanyu Pinyin:
Zhōngguó ;
Tongyong Pinyin:
Jhongguó;
Wade-Giles (Mandarin):
Chung¹kuo²) is a
cultural region, an ancient
civilization, and a
national or
multinational entity in
East Asia. The civilization is one
of the world's oldest, consisting of
states and
cultures dating back more than six
millennia. Zhang Heng (Chinese:
張衡;
pinyin:
Zhāng
Héng;
Wade-Giles: Chang Heng) (AD
78–139)
was an
astronomer,
mathematician,
inventor,
geographer,
artist,
poet,
statesman, and
literary scholar of the
Eastern Han Dynasty in ancient
China. He had extensive knowledge of
mechanics and gears, applying this
knowledge to several of his known
inventions. Shen Kuo or Shen
Kua (Chinese:
沈括;
pinyin:
Shěn Kuò)
(1031–1095) was a
polymathic
Chinese
scientist and statesman of the
Song Dynasty (960–1279). Excelling
in many fields of study and statecraft,
he was a
mathematician,
astronomer,
meteorologist,
geologist,
zoologist,
botanist,
pharmacologist,
agronomist,
archaeologist,
ethnographer,
cartographer,
encyclopedist,
general,
diplomat,
hydraulic engineer,
inventor,
academy chancellor,
finance minister, governmental state
inspector, poet, and musician..